VA loans are offered in both fixed-rate and adjustable-rate mortgages (ARM) to eligible Veterans and active-duty military members. The choice between a fixed-rate and ARM can be a tricky one. The good news is that both options come with their own set of advantages and with favorable VA interest rates.
Let’s explore each mortgage type and highlight significant differences between the two to help choose the right one for you.
What is a VA Fixed-Rate Mortgage?
VA fixed-rate mortgages offer Veterans stability in terms of interest rates and monthly payments. With a fixed-rate mortgage, the interest rate remains constant throughout the entire duration of the loan. This means that regardless of any fluctuations in the broader market or economy, the interest rate and subsequent monthly principal will remain the same.
Are VA Loans Fixed-Rate?
VA loans can be fixed rate or adjustable. Veterans and service members have the option to select between the two types. The choice depends on the individual's preference and financial situation.
What is a VA Adjustable-Rate Mortgage?
A VA adjustable-rate mortgage (ARM) is another type of home loan available to Veterans that offers an initial fixed interest rate for a predetermined period, typically ranging from 1 to 5 years. After this fixed-rate period ends, the interest rate adjusts periodically based on market conditions. The adjustments are typically made annually, but they can occur more frequently depending on the terms of the loan.
Differences Between VA Fixed and Adjustable-Rate Mortgages
After understanding what exactly fixed- and adjustable-rate mortgages are, let’s dive a little deeper into what separates the two.
Monthly Payment Predictability
Borrowers can more accurately budget their monthly expenses with a VA fixed-rate mortgage since the principal and interest portions of the payment remain unchanged over the loan’s life. This stability is especially valuable for individuals who prefer consistency in their financial planning.
VA ARMs offer lower initial rates, but after the fixed-rate period, the rate adjustment can lead to fluctuations in monthly payments. These changes can work in the borrower's favor if rates decrease, but they can also result in higher payments if rates rise.
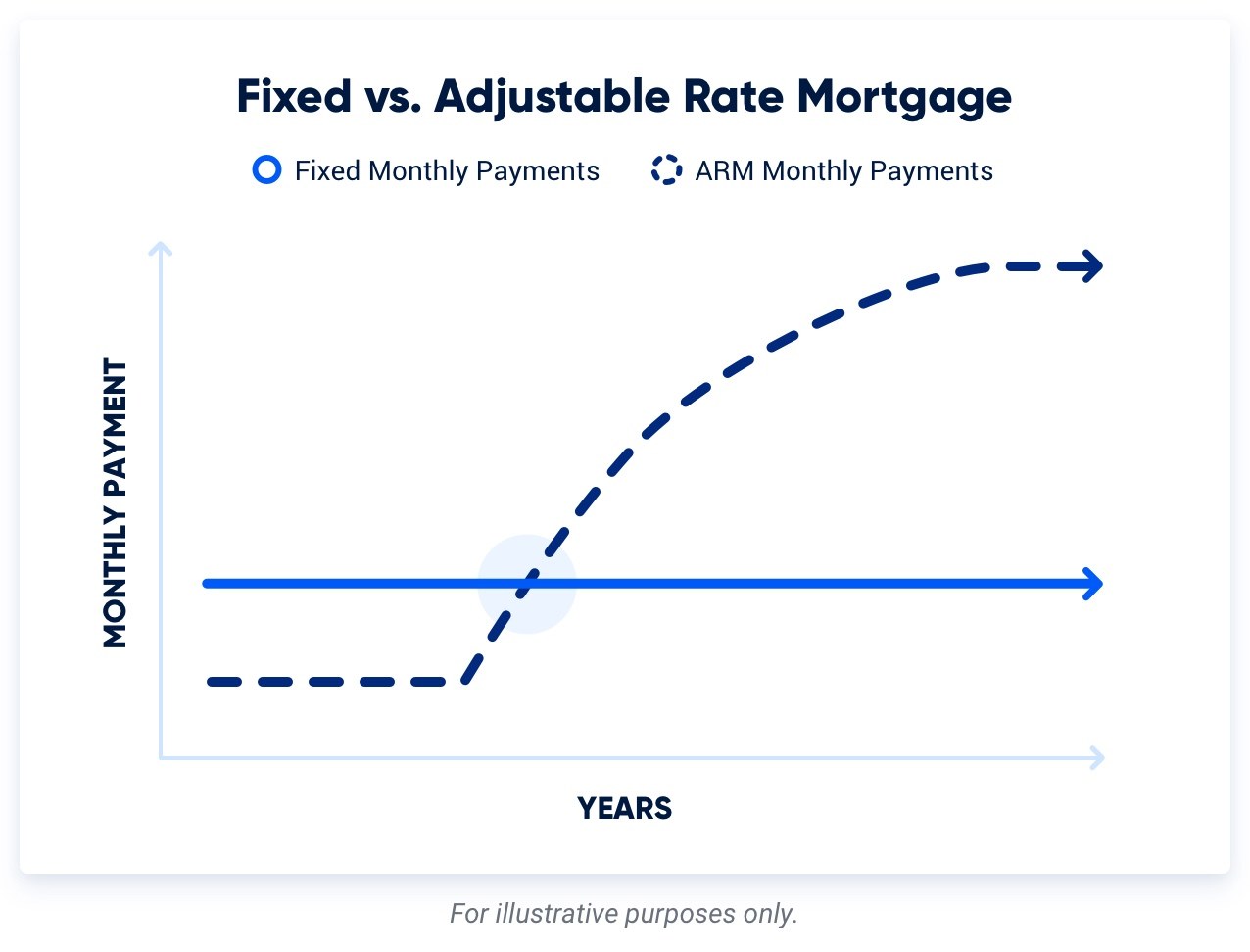
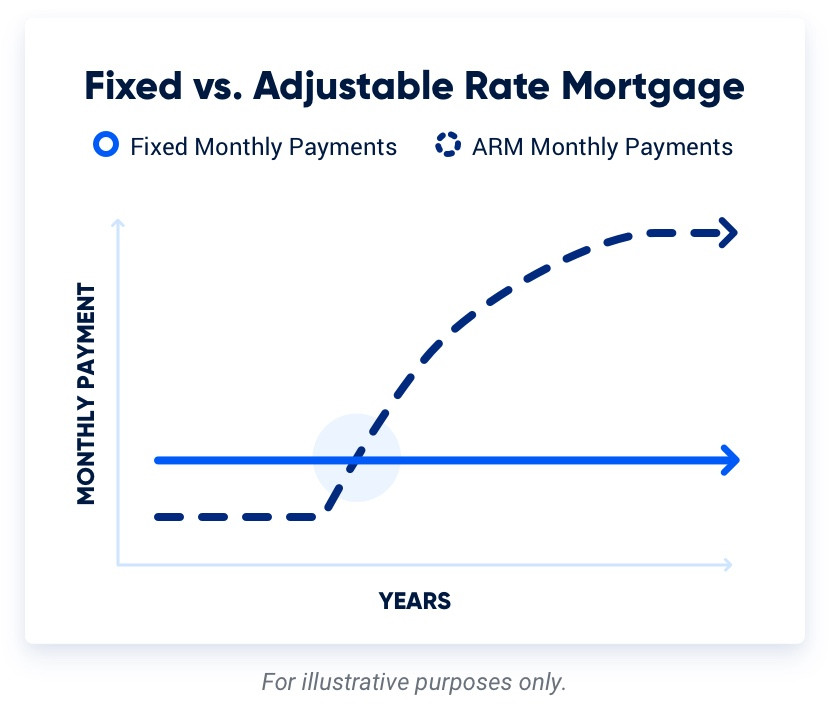
Long-Term Financial Planning
Choosing a VA fixed-rate mortgage can be beneficial for buyers who plan to reside in the home for the foreseeable future. Borrowers can reliably anticipate the total interest paid over the loan term and make accurate projections for their future financial goals. They can also always look to refinance if mortgage rates fall enough to make it worthwhile.
VA adjustable-rate mortgages might be more suitable for borrowers who plan to sell or refinance their loan before the fixed-rate period ends. If you know you will be moving or refinancing within a few years, an ARM can offer lower initial rates, potentially resulting in significant interest savings. Every prospective buyer’s situation is different.
Economic Market Influence
VA fixed-rate mortgages protect borrowers from future interest rate increases, regardless of market conditions. This provides peace of mind and stability, especially during periods of rising interest rates.
On the other hand, VA ARMs are influenced by market conditions. If market interest rates decrease, borrowers may benefit from lower monthly payments. However if rates rise, monthly payments can increase and possibly result in financial instability.
Risk Tolerance and Future Plans
VA fixed-rate mortgages can be suitable for homeowners who prefer stability and have a lower risk tolerance. Ideally, this type of loan is perfect for those planning to stay in their homes for an extended period or seeking consistency in their mortgage payments.
VA adjustable-rate mortgages might be more appropriate for homeowners with a higher risk tolerance and shorter-term housing plans. If you anticipate a change in your financial situation or plan to move or refinance in the near future, an ARM may offer more initial savings.
VA ARM and Fixed-Rate Mortgage Similarities
Both VA fixed-rate mortgages and ARMs offer various loan term options, typically ranging from 15 to 30 years. This allows borrowers to choose the number of years they’ll spend paying off the loan and select a loan term that suits their financial circumstances.
Credit qualifications for VA fixed-rate mortgages and ARMs are very similar since the VA doesn’t set a minimum credit score requirement. Most VA mortgage lenders want to see a FICO credit score of at least 620 for both loan types. Some lenders will approve lower scores, but usually with additional requirements. The higher your credit score, the more likely you’ll be able to get either an ARM or a fixed-rate mortgage.
VA Fixed vs. Adjustable-Rate Mortgages: Which is Better?
Many borrowers want to know which option best suits their unique financial goals and circumstances. Below we outlined some common factors that can influence your decision when choosing a VA loan interest rate.
| VA Fixed-Rate | VA Adjustable-Rate |
|---|---|
| Long-term ownership | Short-term ownership |
| Rising interest rates | Falling interest rates |
| Borrower has fixed income | Borrower expects income increase |
| Affordability of current interest rates | Availability of VA hybrid ARMs |
VA Fixed-Rate Mortgages May Work Best If
1. You Plan to Occupy the Home Long-Term
If you plan to live in the house for more than a few years, a fixed-rate mortgage may be best for you. ARMs often have lower initial rates than fixed-rate mortgages, which can increase significantly over time. Choosing a VA fixed-rate mortgage protects you from these rate increases.
2. Interest Rates are Rising
If you believe that interest rates are likely to rise in the future, a fixed-rate mortgage can lock in the current rate and protect you from future increases.
3. You Have a Fixed Income
If you're on a fixed income, such as a retirement pension, having a principal and interest payment that won't change can be especially beneficial. Unexpected increases in your mortgage payment could strain your budget.
4. You Can Afford Current Interest Rates
If you can afford the home you want with the current fixed rates, it might make more sense to choose a fixed-rate mortgage. You'll have the certainty of fixed principal and interest payments and won't have to worry about possible future rate increases.
VA Adjustable-Rate Mortgages May Work Best If
1. You Plan to Occupy the Home Short-Term
If you’re planning to reside in the home for only a few years, a VA ARM may be the option for you. ARMs often have lower initial rates than fixed-rate mortgages, so if you sell the home before the rate adjusts upward, you could save money.
2. Interest Rates are Falling
If you believe that interest rates will fall in the future, then an ARM could be advantageous. However, predicting interest rates is notoriously difficult, so this is a high-risk strategy.
3. Your Annual Income is Expected to Increase
If you’re expecting a salary increase, an ARM could be the right option for you. This would allow you to budget for higher mortgage payments in the future when the rate adjusts.
4. VA Hybrid ARMs are Available
The VA offers hybrid ARMs that have a period of fixed interest rates (typically for the first 3-5 years) and then adjust annually. This combines some stability of a fixed-rate loan with the potential benefits of an adjustable-rate loan. VA ARMs also have what’s known as a 1/1/5 cap, which means the most the rate can increase in the first and all subsequent years is 1 percentage point, up to no more than 5 percentage points from where you started.
How We Maintain Content Accuracy
Our mortgage experts continuously track industry trends, regulatory changes, and market conditions to keep our information accurate and relevant. We update our articles whenever new insights or updates become available to help you make informed homebuying and selling decisions.
Current Version
Jul 1, 2025
Written ByChris Birk
Added video, "Fixed Rate vs. ARMs"
Related Posts
-
 What is the VA Seller Concession Rule?Seller concessions with a VA home loan can save Veteran homebuyers thousands of dollars, but cannot exceed 4% of the loan.
What is the VA Seller Concession Rule?Seller concessions with a VA home loan can save Veteran homebuyers thousands of dollars, but cannot exceed 4% of the loan. -
 VA Loan Discount PointsPurchasing discount points on a VA loan can be a good investment for Veterans looking to lower their interest rate.
VA Loan Discount PointsPurchasing discount points on a VA loan can be a good investment for Veterans looking to lower their interest rate.
